
- Details
- Written by: Mike Leary
- Category: Science
Human biological sex is often thought of in binary terms male or female but the science tells a more complex story. A wide range of biological, genetic and developmental factors shape what we understand as sex. For millions of people, these factors don’t align with traditional male or female classifications. This complexity is not just theoretical it has real-life implications for medicine, law, identity documents and social life.
Read more: Understanding human sex diversity requires moving beyond simple definitions
- Details
- Written by: Mike Leary
- Category: Science
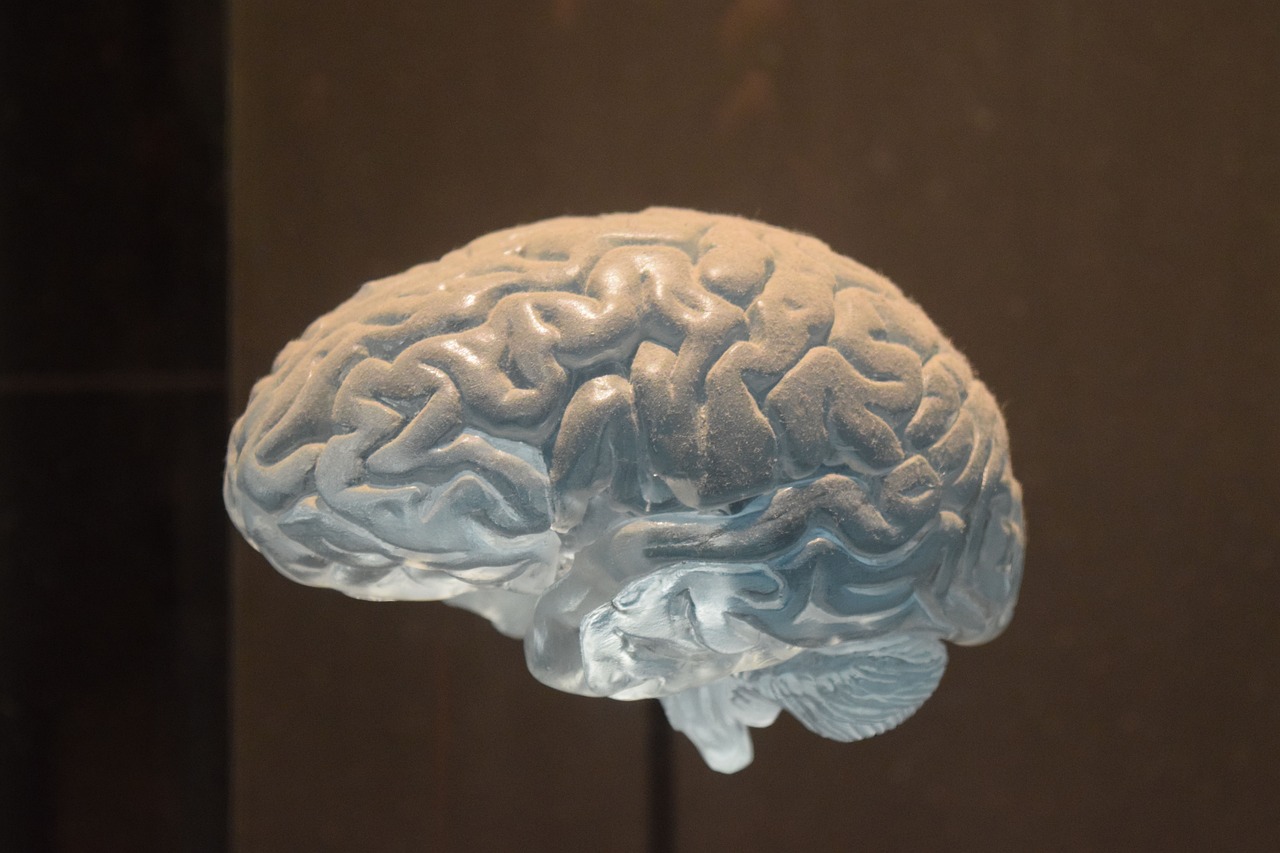
A groundbreaking study has identified a physical mechanism in the brain that connects memories occurring within a short time frame. The discovery shows that dendrites - tiny, branch-like structures of neurons - are responsible for linking these memories, not the main cell bodies of the neurons. This research may change how scientists understand memory formation and its role in disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
Read more: New study reveals how dendrites physically connect closely timed memories

- Details
- Written by: Mike Leary
- Category: Science
The Physics of Perception – How Our Brain Constructs Reality Perception feels effortless. We open our eyes and see the world. We hear sounds, feel textures, and smell scents without questioning how it happens. But what if the reality we experience is just a construct? Neuroscience and physics suggest that our perception is not a direct representation of the world. Instead, the brain interprets sensory data and creates a version of reality that helps us navigate life.

- Details
- Written by: Mike Leary
- Category: Science
Collective Intelligence – Can Humanity Become a Superorganism? Humans have always thrived on collaboration. From ancient tribes to modern cities, our ability to work together has shaped civilization. But as technology advances, some researchers believe we may be evolving into something more—a superorganism. This idea suggests that humanity is becoming a vast, interconnected system, where individuals function like cells in a larger body. Could collective intelligence reshape the future of human existence? Science, philosophy, and psychology suggest it might.
Read more: Collective Intelligence – can humanity become a superorganism?
